Digital Assets Management (DAM) Protocol
Introduction
This protocol outlines the guidelines and procedures for managing digital assets within Gaya Studios, ensuring efficient organization, secure storage, and streamlined access for both in-house studio and remote teams.
Asset Management System (AMS)
This section outlines the Asset Management System (AMS) for 3D assets used in development projects. The system aims to streamline the workflow between the Art and Development teams, ensuring efficient management and backup of assets.
Components
-
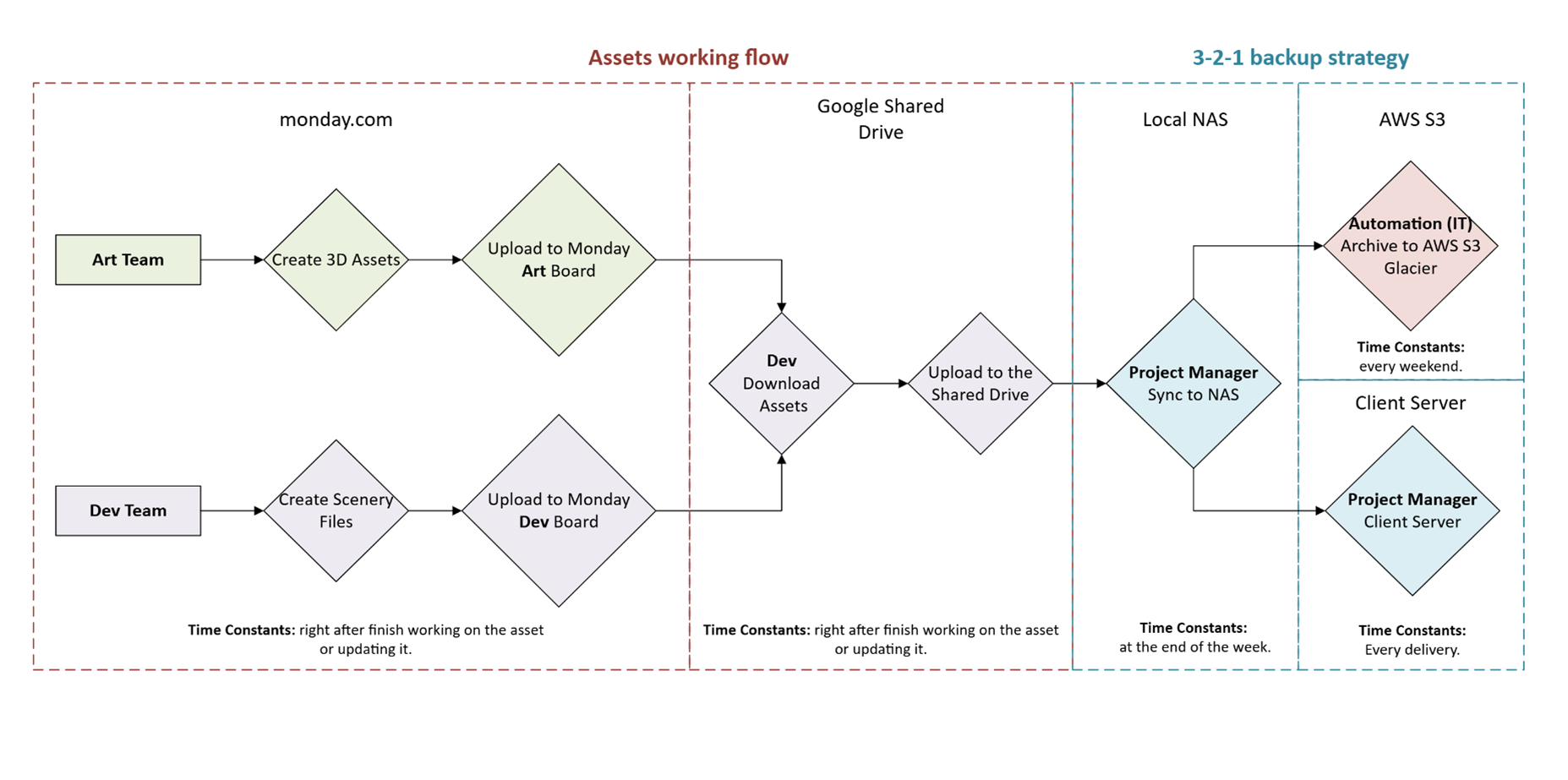
Assets working flow: streamlines 3D asset management between Art and Development teams. It uses Monday.com for project management and Google Drive for cloud storage.
- Monday.com: A project management platform used for both the Art and Development teams.
- Google Drive Shared Drive: A cloud storage platform used by the Development team to manage project files.
-
3-2-1 backup strategy: ensures asset safety with local NAS storage, AWS S3 Glacier for long-term archiving, and a client server for file delivery.
- Local NAS: A Network Attached Storage device used for local project access and syncing with AWS.
- AWS S3 Glacier Deep Archive: A cloud storage service for long-term, low-cost archiving of project data.
- Client Server: This server, most often an FTP server, is used for delivering files to the client.
More information about how to setup those components in the component setup page.
Flowchart
Workflow
Asset Creation (Art Team):
- Responsibility: art team members.
- Time Constants: right after finish working on the asset or updating it.
- Platform: Monday.com
- The Art Team creates 3D assets.
- The assets are exported in GLTF MSFS format.
- The export and work files are uploaded to a dedicated ART board within Monday.com.
- After each fix or change, a new version of the model will be uploaded to Monday.com using the version option. This ensures the Monday.com board always reflects the latest model and work files.
Project Setup (Dev Team):
- Responsibility: Dev team leader.
- Time Constants: in the beginning of the production
- Platform: Google shared drive.
- The Development lead creates a new project within Google Drive Shared Drive. (See Project (MSFS) file structure)
- This project will be shared with all project developers.
Asset Integration (Dev Team):
- Responsibility: Dev team members.
- Time Constants: when starting to work on each task.
- Platform: Google shared drive.
- The Dev team downloads the relevant 3D assets from the Monday.com board.
- Assets should be categorized and saved in their respective subfolders: for example, work files in 'source', 3D models in 'modelLib', and textures in 'texture'. For more information see Project (MSFS) file structure protocol.
Scenery Development (Dev Team):
- Responsibility: Dev team members.
- Time Constants: when finish working on each task.
- Platform: moday.com.
- The Dev team creates a scenery XML file to integrate the downloaded assets with level design.
Asset Consolidation (Dev Team):
- Responsibility: Dev team members and dev leader.
- Time Constants:
- Each team member, when finish working on each task.
- The dev leader, at the end of each working day, checking and organizing the project.
- Platform: Google shared drive.
- Both the scenery XML file and the downloaded 3D assets are uploaded to the project folder within the Shared Drive.
Data Synchronization:
- Responsibility: project manager
- Time Constants:
- Daily automatic backup to a dedicated backup volume on the NAS.
- Weekly synchronization of the project folder in the Shared Drive with the main NAS storage.
- Platform: NAS.
- The project folder in the Shared Drive needs to be synced with the local NAS in two parts:
- Daily automatic backup to a dedicated backup volume on the NAS for immediate redundancy.
- Weekly synchronization of the entire project folder with the main NAS storage.
Backup & Archive:
- Responsibility: automation (IT manager)
- Time Constants: every weekend.
- Platform: AWS S3.
- The NAS automatically uploads all project data to AWS S3 Glacier Deep Archive for secure long-term storage.
Delivery to Client:
- Responsibility: Project manager.
- Time Constants: Every delivery.
- Platform: Client server.
- The project manager delivers the final assets to the client via the client server.
Projects file structure
*see protocol
Search and retrieval
The Asset Management System (AMS) leverages a combination of platform-specific search functionalities and standardized metadata to ensure efficient retrieval of assets across various storage solutions. Here's a breakdown of search and retrieval methods for each platform:
Monday.com
- Search Functionality: Keyword search within board names, descriptions, file names, and update comments. Users can filter by file type, creation date, and assigned team/member.
- Retrieval Methods: Direct download of files uploaded to Monday.com boards. Version history allows access and restoration of previous file versions.
Google Shared Drive
- Search Functionality: Keyword search within file names, and descriptions. Users can filter by file type, owner, creation date, and shared access level.
- Retrieval Methods: Direct download of files from Google Shared Drive. Version history enables restoring previous versions.
Local NAS
- Search Functionality: File-level search based on file names and limited metadata indexing (depending on NAS capabilities). Advanced search might require additional file tagging or third-party indexing tools.
- Retrieval Methods: Direct download of files from the NAS device. Version control capabilities may vary depending on the specific NAS solution.
AWS S3 Glacier Deep Archive
- Search Functionality: Search by filename and some basic metadata associated with the file object in S3. Advanced search capabilities are limited due to the archive's focus on low-cost, long-term storage.
- Retrieval Methods: Files must be restored from Glacier Deep Archive to S3 Standard storage class before download or use. Retrieval times can vary depending on the data quantity.
Optimizing Search and Retrieval Across Platforms
- Standardized Metadata: Maintain consistent tagging and descriptions for assets across all platforms using a defined metadata schema. This ensures consistent search results regardless of the storage location.
- Regular Indexing: Schedule periodic metadata updates for NAS and S3 storage to keep search indexes current.
- User Training: Educate users on the search functionalities and limitations of each platform to facilitate efficient asset discovery.
By understanding the search and retrieval strengths of each platform and implementing consistent metadata practices, users can leverage the AMS for seamless asset discovery across the entire project ecosystem.
Permissions and access control
This section outlines the permission and access control measures implemented to safeguard digital assets and ensure authorized access within Gaya Studios.
Access Levels
- Full Access: Granted to core team members (Art Directors, Lead Artists, Project Managers, and IT personnel) who require unrestricted access to all digital assets and system functionalities.
- Read-Only Access: Granted to team members (Junior Artists, Designers, and other support staff) who need to view and reference assets for their work but are restricted from making modifications.
- Limited Access: Granted to external collaborators (freelancers, contractors) who have specific access to designated project assets and limited functionalities within the AMS.
Access Control Mechanisms
- User Authentication:
- Strong password requirements (combination of uppercase, lowercase, numbers, and special characters)
- Regular password changes
- Two-factor authentication (2FA) for enhanced security
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
- Assigning specific roles to users based on their responsibilities and granting appropriate permissions
- Regular review and update of role assignments to maintain security
- File and Folder Permissions:
- Implementing detailed file and folder permissions to control access to specific assets
- Limiting access to sensitive information and proprietary assets
- Network Security:
- Secure network infrastructure with firewalls and intrusion detection systems
- Encrypted data transmission for protecting sensitive information
- Regular Security Audits:
- Conducting regular security audits to identify and address vulnerabilities
- Staying updated with the latest security best practices and industry standards
Best Practices
- Limit Access to Necessary Personnel: Grant access only to individuals who require it for their specific tasks.
- Monitor and Log Access: Track user activity and access logs to identify suspicious behavior.
- Regularly Review and Update Permissions: Ensure that permissions are aligned with current roles and responsibilities.
- Educate Users: Conduct regular training sessions to raise awareness about security best practices and potential threats.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a well-defined incident response plan to address security breaches and data loss.